Smart Manufacturing Defined
- ehdtech
- Apr 11, 2018
- 3 min read
Definitions of smart manufacturing are often too abstract to be understood. Claims that it connects billions of machines and people confuse rather than clarify. More specifics are needed.
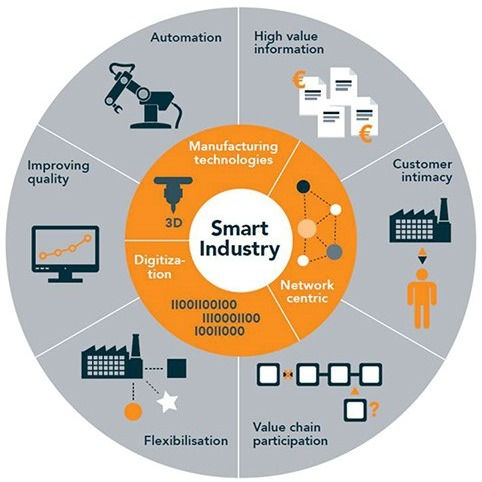
Smart Manufacturing is …
Flat
When people talk about businesses being “flat,” they’re referring to eliminating the layers of management between the top and the bottom of the organizational pyramid. In the factory, they are referring to the manufacturing technology stack that connects and helps control the production process from the plant floor to business planning and logistics.
Smart manufacturing flattens both of these hierarchies by providing more access to more business data to more people, which otherwise would have been obtained through the slow process of information moving up and decisions coming down the hierarchy.
Stakeholders should use smart technologies that make appropriate data available via dashboards to those who need it, when they need it. Early adopters, for example, provide plant floor operators with specific machine and production-quality data while delivering executives factory-level data with exception alerts.
Data-Driven
Though it is not a new concept to get the right data to the right place at the right time -- so operators and business leaders can make better-informed decisions -- smart manufacturing finally makes this possible. With the internet, big data, analytics and the cloud, decision makers throughout the company can get information with a few taps on their smartphone or tablet.
Sustainable
Sustainability in business means the ongoing economic, social and environmental viability of the company -- the so-called triple bottom line. Smart manufacturing supports achieving all three together by providing the real-time data you need to capture opportunities and keep costs down and productivity up while better understanding waste and material losses and monitoring your workforce challenges.
Using smart manufacturing, companies can gather the data needed to address issues of social responsibility, such as customer demands for fair trade and work practices. With smart manufacturing, companies have set up trace-ability in the supply chain to provide the information needed to prove suppliers are operating in a sustainable, fair way.
Agile
The faster data gathering, processing and communication made possible by smart manufacturing enables faster decision making. Opportunities or problems that are identified early and dealt with quickly help decision makers respond to changes in the marketplace, whether global or local and to shift production to where it is most profitable.
Perhaps the best example of this is the ability to monitor and feed sales into executive decision making dashboards, so quick increases or decreases in demand can be met with changes to production.
People Oriented
Smart manufacturing is about helping people do their jobs better. For example, providing factory operators with machine interfaces that deliver production and quality data allows them to act in real time to address slowdowns or quality variances. Delivering information to procurement executives about a hitch in a critical supply chain enables them to quickly ramp up alternative sourcing.
Profitable
When conversations about smart manufacturing focus on the technology that connects equipment and people in ways never before possible, they miss the point. Companies implement smart manufacturing to easily and effectively make a profit.
Research by the MPI Group found that 69% of manufacturers credit their use of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies for increasing their profitability. Top processes representing the best opportunities to leverage the IoT cited by the survey respondents include document management, warehousing, shipping/logistic/transportation and packaging.
Innovative
When you provide everyone in your company with access to the data they need to solve problems you change the mindset of everyone in your company. They engage in continuously improving work practices to eliminate waste and drive value.
Current
Businesses do not have to wait for new technology to be perfected to launch a smart manufacturing initiative. Disruption comes and goes before you realize it is even coming.
By understanding how smart manufacturing’s attributes relate a specific tactic and contribute to achieving a business goal, you can make smart decisions about how to deploy the technologies and move forward in your smart manufacturing journey.
The Sustained Quality Group Solution
The Sustained Quality Group offers 24-hour portal access to custom, accurate, real-time data and analytical tools to drive positive results within your organization.
To speak with a SQG representative in your area, please call 615-953-1907.
Clemons, John. (2018). “The Anatomy Of Smart Manufacturing”. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2018/03/19/the-anatomy-of-smart-manufacturing/#725a0b5b6a6c.






























Comments